Introduction to Six Sigma
Six Sigma is a data-driven methodology that aims to improve business processes by reducing defects and minimizing variability. It is widely used in manufacturing, healthcare, IT, and many other industries to enhance quality and efficiency.
What is Six Sigma ?
Six Sigma is a structured approach to process improvement that focuses on identifying and eliminating defects in a process. The goal is to achieve near-perfect quality by reducing defects to 3.4 per million opportunities (DPMO). Six Sigma is not a new term, probably you are reading this article because you want to know some key facts about ‘Six Sigma’, and I would you assure you that you have come to the right place.
Six Sigma was originally introduced by Bill Smith of Motorola in United States of America in 1986 . He is often referred to as the “Father of Six Sigma“. His ideas gained traction, and Motorola officially adopted Six Sigma as a company-wide strategy in 1986. The methodology later spread across various industries, with companies like General Electric and Toyota refining and expanding its applications.

Do you know till date there are approx 40 companies who have successfully implemented Six Sigma
Motorola’s Quality Crisis and the Need for Six Sigma
During that time, Motorola was in trouble as the quality of its products started declining, which ultimately impacted profitability. The company faced increasing competition and customer dissatisfaction, making it imperative to address quality issues before they risked being phased out of business. Recognizing the urgency, Motorola embraced Six Sigma as a structured, data-driven approach to process improvement, setting a new standard in quality management.
Another company General Electric implemented and adopted Six Sigma through proper Six Sigma training from Motorola. Motorola saved millions of dollar and six sigma added US $ 300 million to GE profit.
🏆 𝐁𝐞𝐬𝐭 𝐁𝐨𝐨𝐤 ( 🎭 𝐌𝐮𝐬𝐭 𝐑𝐞𝐚𝐝 )
Click here to Buy from Amazon
As of today many business and manufacturing sectors uses this to improve the overall quality of process by identifying and eliminating the root cause and minimizing the variability in process. Six sigma is bringing higher customer satisfaction, and better profit.
Six Sigma is structured, data driven approach to eliminate or reduce defects from any process whether its is manufacturing or service. Six Sigma is denoted by Greek symbol “6σ” and is a process which refers to 99.99966%.
In practical terms, a Six Sigma process produces 99.99966 % defect free products which is equivalent to 3.4 defects per million opportunities (DPMO).
Six Sigma aims to improve quality by finding defects, determining their root cause, and improving processes. The philosophy in Six sigma is to reduce output process variations and has now become a new success mantra in the modern world.
What is σ in 6σ and Why we have 6 σ and not 5 σ or 7 σ ?
In Six Sigma, σ (sigma) represents the standard deviation of a process. The standard deviation measures the variation in a set of data, indicating how much the data points deviate from the mean. A lower standard deviation means a more consistent and predictable process, whereas a higher standard deviation indicates more variability and defects.
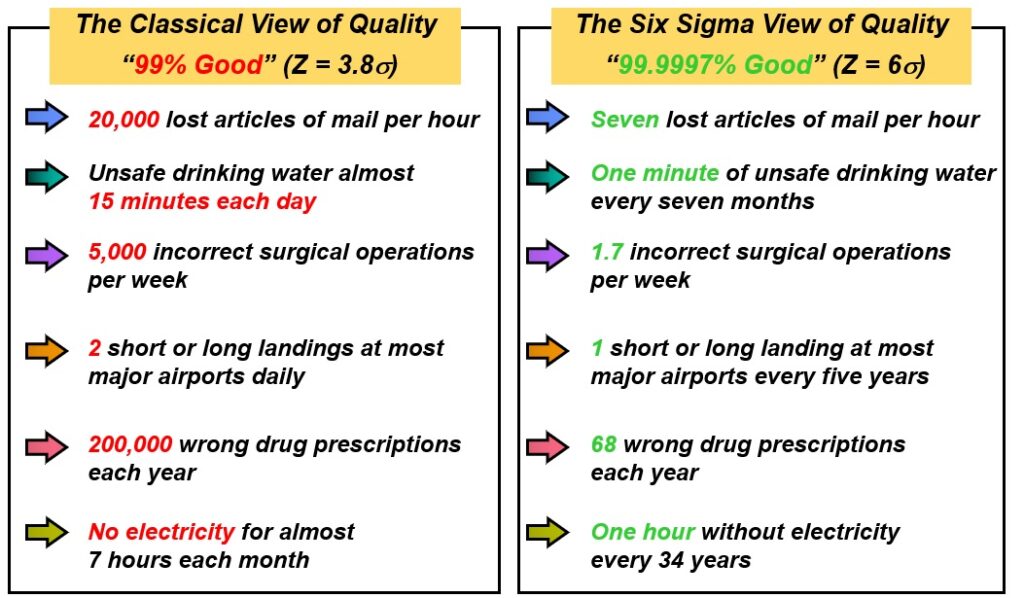
The choice of 6σ (Six Sigma) is based on achieving an exceptionally low defect rate. Here’s why:
- Statistical Justification: A process that operates at a Six Sigma level has only 3.4 defects per million opportunities (DPMO), which is an extremely high level of quality. This ensures near-perfection in production and service processes.
- Comparison to Other Sigma Levels:
- 1σ: 691,462 defects per million (69% error rate)
- 2σ: 308,538 defects per million (30% error rate)
- 3σ: 66,807 defects per million (6.7% error rate)
- 4σ: 6,210 defects per million (0.62% error rate)
- 5σ: 233 defects per million (0.023% error rate)
- 6σ: 3.4 defects per million (0.00034% error rate)
- Business Impact: At 5σ, there are still too many defects per million, which may be costly for businesses. On the other hand, 7σ would require an exponentially higher investment with diminishing returns, making it impractical for most industries. At 7σ process 0.019 defects per million opportunities.
- Practical Implementation: Six Sigma balances quality and cost-effectiveness. It allows companies to maintain high-quality products and services while still being feasible to implement.
Based on above data, we can summarize that 5σ process will not meet customer requirements, and 7σ will not add significant value and probably will add significantly to the cost. That’s is why we have a tradeoff 6σ which is close to perfection, and that makes it a more attainable and realistic goal to achieve. Airlines and Medical industries cannot afford to work at 6σ. operates at higher Sigma level than 6σ (Close to 9 or 10 σ).
In conclusion, Six Sigma (6σ) is chosen because it provides a statistically sound, achievable, and cost-effective method for process improvement, reducing defects to an extremely low level while remaining practical for businesses to implement.
🏆 𝐁𝐞𝐬𝐭 𝐁𝐨𝐨𝐤 ( 🎭 𝐌𝐮𝐬𝐭 𝐑𝐞𝐚𝐝 )
Click here to Buy from Amazon
Six Sigma Career Choices and Salary Prospects
Six Sigma professionals have a wide range of career opportunities in industries such as manufacturing, healthcare, finance, and IT. Roles include:
- Six Sigma Analyst
- Process Improvement Specialist
- Quality Engineer
- Operations Manager
- Six Sigma Consultant
Salary Prospects for 2025
Six Sigma professionals continue to be in high demand across various industries, leading to attractive salary packages. The expected salary ranges based on Six Sigma certification levels in 2025 are:
- Six Sigma Yellow Belt: $55,000 – $75,000
- Six Sigma Green Belt: $80,000 – $100,000
- Six Sigma Black Belt: $100,000 – $130,000
- Six Sigma Master Black Belt: $130,000 – $160,000
In addition to higher salaries, Six Sigma professionals often enjoy enhanced job security, career growth opportunities, and leadership roles in their organizations. Companies value Six Sigma expertise for its ability to drive cost reductions, improve efficiency, and enhance overall business performance.
People Roles in Six Sigma
In order to execute six sigma projects, you will need a team which comprised of highly trained professional people all trained on Six sigma methodologies and principles. Six Sigma took the concept of martial arts concepts to define its belts to designate a level of methodological mastery over Six sigma.
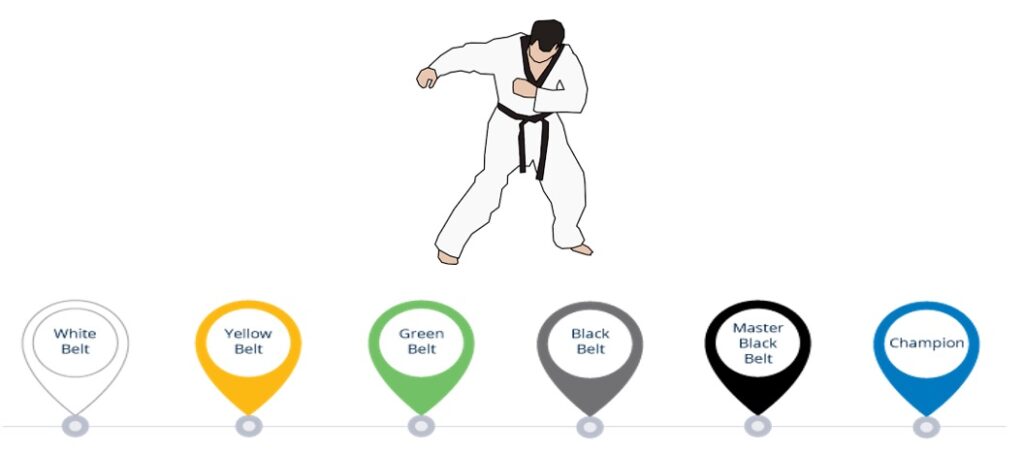
Executive : Normally the CEO and Top executives of company.
Champion: Mostly the upper management who is sometimes the sponsor as well. Executives select the Champions. All the financial decision are approved by Champions.
Master Black Belts: Champions select the Master Black Belts who work directly under them. They lead and train black belts and Green belts and also helps to identify company with some future six sigma projects for company.
Black Belts: Under the Master black belts, we have black belts who actually execute six sigma project and in short lead project from start to finish.
Green Belts : Under the black belts, we have green belts who do major part of work and support black belt in execution of six sigma methodologies and statistical techniques.
Yellow Belts : They have basic knowledge of six sigma. They may or may not support directly but may participate in some project task in order to gain some knowledge and experience. They sometimes could be silent listeners as well.
White Belts :They are totally new to Six sigma and are learning new tools and techniques related to Six sigma every now and then
Key Principles of Six Sigma
- Customer Focus: The ultimate goal is to meet or exceed customer expectations.
- Data-Driven Decision Making: Decisions are based on data and statistical analysis.
- Process Improvement: Continuous improvement is emphasized through various techniques.
- Proactive Problem Solving: Anticipating issues before they arise.
- Teamwork and Collaboration: Six Sigma requires collaboration across different departments.
Let’s take an example of Dominos Pizza

Dominos claim that they deliver all their pizza within 30 mins. If they fail to meet this, they will refund 100% money back to customer. How many times you can recall that you have ordered a pizza from Dominos and it would have arrived after 30 mins. Dominos pizza delivery process operates at 99.9997% or 6σ level. Their CTQ is time to deliver the pizza to customer within 30 mins.
Six Sigma Benefits :
- Increased Customer Satisfaction
- Increased Revenue
- Increased Customer Satisfaction
- Cost Reduction
- Reduction in Process variation
- Boost in Employee morale
- Increased participation
Watch this animated YouTube video for details :
🏆 𝐁𝐞𝐬𝐭 𝐁𝐨𝐨𝐤 ( 🎭 𝐌𝐮𝐬𝐭 𝐑𝐞𝐚𝐝 )
Click here to Buy from Amazon
Six Sigma Methodologies
The principles of Six Sigma are executed through methodologies, or roadmaps to improvement, like a workflow. Two main methodologies are DMAIC and DMADV.
- DMAIC ( Define, Measure, Analyze, Improve and Control )
- DMADV ( Define, Measure, Analyze, Design, and Verify )
If you want to understand when do we use DMAIC and when do we use DMADV, then watch this video on Difference between DMAIC vs DMADV –
If you want to understand the complete all the steps of Six Sigma DMAIC , then watch this below video. :
FAQs on Six Sigma
- What industries use Six Sigma? Many industries, including manufacturing, healthcare, finance, and IT, use Six Sigma to improve quality and efficiency.
- How is Six Sigma different from Lean? Six Sigma focuses on reducing defects and variation, while Lean aims at eliminating waste and improving process flow.
- What is the difference between DMAIC and DMADV? DMAIC improves existing processes, while DMADV is used for designing new processes or products.
- Do I need prior experience for Six Sigma certification? No prior experience is required for entry-level certifications, but advanced levels may need experience in process improvement.
- What software is used in Six Sigma projects? Common software includes Minitab, JMP, and Microsoft Excel for statistical analysis.
- Is Six Sigma only for manufacturing? No, Six Sigma is applied in many fields, including healthcare, IT, and finance.
- What is a Six Sigma project example? A project could involve reducing defect rates in a production line or improving patient wait times in a hospital.
- How long does it take to get certified? Certification times vary, typically ranging from a few weeks to several months.
- What are the benefits of Six Sigma certification? Benefits include higher salary, career growth, and improved problem-solving skills.
- Can I learn Six Sigma online? Yes, many online platforms offer Six Sigma training and certification programs.
I hope this blog helped in understanding the basic concept in a simplified manner, watch out for more such stuff in the future.
📢📢 𝑺𝒐𝒄𝒊𝒂𝒍 𝑴𝒆𝒅𝒊𝒂 𝑳𝒊𝒏𝒌:
Thanks!!!
For questions please leave them in the comment box below and I’ll do my best to get back to those in a timely fashion. And remember to subscribe to Digital eLearning YouTube channel to have our latest videos sent to you while you sleep.
✍️ 𝓓𝓲𝓼𝓬𝓵𝓪𝓲𝓶𝓮𝓻: Copyright Disclaimer under section 107 of the Copyright Act of 1976, allowance is made for “fair use” for purposes such as criticism, comment, news reporting, teaching, scholarship, education and research. Fair use is a use permitted by copyright statute that might otherwise be infringing. The information contained in this video is just for educational and informational purposes only and does not have any intention to mislead or violate Google and YouTube community guidelines or policy. I respect and follow all terms & conditions of Google & YouTube.









Hello dear,
Thank you for sharing this valuable article.
I am totaly new to six sigma concept, my question is how to find sigma value in our manufacturing proceess to know where we are, it mean:
one sigma
three sigma or
six sigma,
Your kind support is much appreciated in this mater.
Best regards,