Six Sigma is not a new term, probably you are reading this article because you want to know some key facts about ‘Six Sigma’, and I would you assure you that you have come to the right place.
What is Six Sigma ?
Six Sigma is a management strategy which was originally introduced by Bill Smith of Motorola in United States of America in 1986 to reduce variations in manufacturing process. Motorola during that time was in trouble as their quality of products started declining, and which ultimately hampers their profit. They needed to fix this as soon as possible before they are phaseout of business. Till date there are approx 40 companies who have successfully implemented Six Sigma in some form or another.
Another company General Electric implemented and adopted Six Sigma through proper Six Sigma training from Motorola. Motorola saved millions of dollar and six sigma added US $ 300 million to GE profit.
As of today many business and manufacturing sectors uses this to improve the overall quality of process by identifying and eliminating the root cause and minimizing the variability in process. Six sigma is bringing higher customer satisfaction, and better profit.
Six Sigma is structured, data driven approach to eliminate or reduce defects from any process whether its is manufacturing or service. Six Sigma is denoted by Greek symbol “6σ” and is a process which refers to 99.99966%.
In practical terms, a Six Sigma process produces 99.99966 % defect free products which is equivalent to 3.4 defects per million opportunities (DPMO).
Six Sigma aims to improve quality by finding defects, determining their root cause, and improving processes. The philosophy in Six sigma is to reduce output process variations and has now become a new success mantra in the modern world.
What is σ in 6σ and Why we have 6 σ and not 5 σ or 7 σ ?
A sigma is a measure of standard deviation denoted by Greek symbol “σ”. Sigma is a statistical term which measures the process deviation from the process mean or process target.
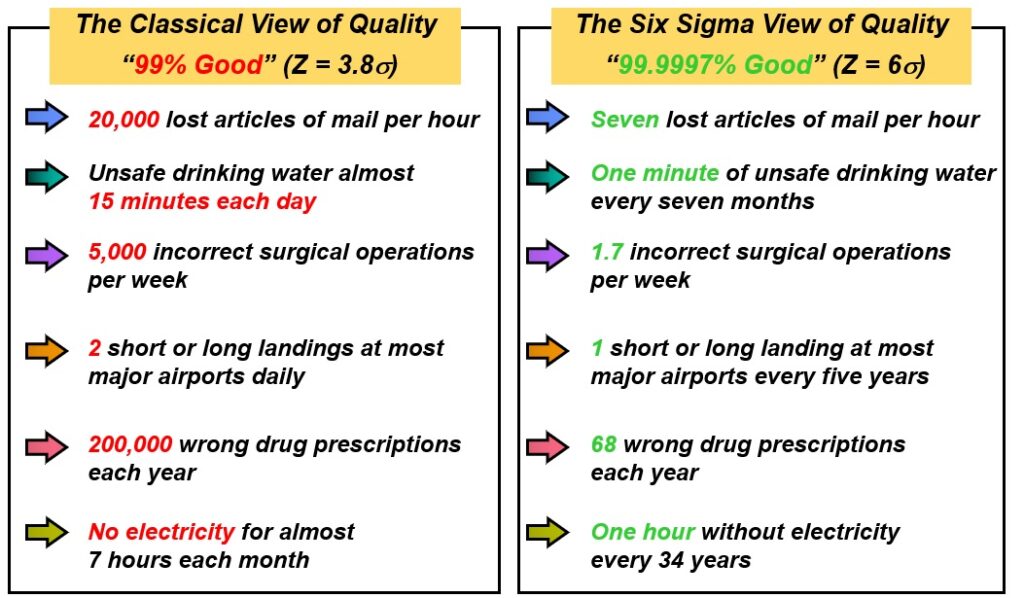
- So 6 times standard deviations or 6σ process will ensure 3.4 defects per million opportunities.
- At 5σ process 233 defects per million opportunities
- At 7σ process 0.019 defects per million opportunities
Based on above data, we can summarize that 5σ process will not meet customer requirements, and 7σ will not add significant value and probably will add significantly to the cost. That’s is why we have a tradeoff 6σ which is close to perfection, and that makes it a more attainable and realistic goal to achieve. Airlines and Medical industries cannot afford to work at 6σ. operates at higher Sigma level than 6σ (Close to 9 or 10 σ).
Let’s take an example of Dominos Pizza

Dominos claim that they deliver all their pizza within 30 mins. If they fail to meet this, they will refund 100% money back to customer. How many times you can recall that you have ordered a pizza from Dominos and it would have arrived after 30 mins. Dominos pizza delivery process operates at 99.9997% or 6σ level. Their CTQ is time to deliver the pizza to customer within 30 mins.
Six Sigma Team
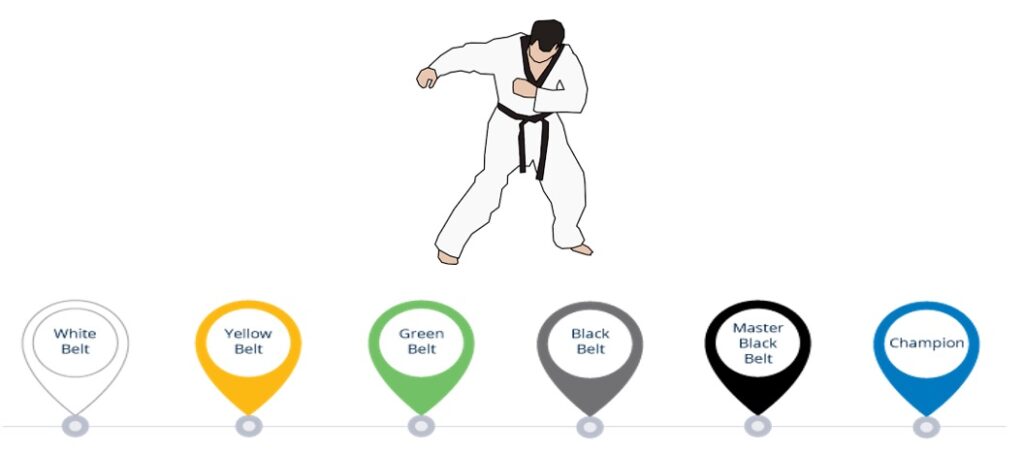
In order to execute six sigma projects, you will need a team which comprised of highly trained professional people all trained on Six sigma methodologies and principles. Six Sigma took the concept of martial arts concepts to define its belts to designate a level of methodological mastery over Six sigma.
Executive : Normally the CEO and Top executives of company.
Champion: Mostly the upper management who is sometimes the sponsor as well. Executives select the Champions. All the financial decision are approved by Champions.
Master Black Belts: Champions select the Master Black Belts who work directly under them. They lead and train black belts and Green belts and also helps to identify company with some future six sigma projects for company.
Black Belts: Under the Master black belts, we have black belts who actually execute six sigma project and in short lead project from start to finish.
Green Belts : Under the black belts, we have green belts who do major part of work and support black belt in execution of six sigma methodologies and statistical techniques.
Yellow Belts : They have basic knowledge of six sigma. They may or may not support directly but may participate in some project task in order to gain some knowledge and experience. They sometimes could be silent listeners as well.
White Belts :They are totally new to Six sigma and are learning new tools and techniques related to Six sigma every now and then
Six Sigma Benefits :
- Increased Customer Satisfaction
- Increased Revenue
- Increased Customer Satisfaction
- Cost Reduction
- Reduction in Process variation
- Boost in Employee morale
- Increased participation
Watch this animated YouTube video for details :
Six Sigma Methodologies
The principles of Six Sigma are executed through methodologies, or roadmaps to improvement, like a workflow. Two main methodologies are DMAIC and DMADV.
- DMAIC ( Define, Measure, Analyze, Improve and Control )
- DMADV ( Define, Measure, Analyze, Design, and Verify )
If you want to understand when do we use DMAIC and when do we use DMADV, then watch this video on Difference between DMAIC vs DMADV – >> YouTube Video Link
If you want to understand the complete all the steps of Six Sigma DMAIC , then watch this below video. :
For questions please leave them in the comment box below and I’ll do my best to get back to those in a timely fashion. And remember to subscribe to Digital eLearning YouTube channel to have our latest videos sent to you while you sleep.





Hello dear,
Thank you for sharing this valuable article.
I am totaly new to six sigma concept, my question is how to find sigma value in our manufacturing proceess to know where we are, it mean:
one sigma
three sigma or
six sigma,
Your kind support is much appreciated in this mater.
Best regards,